UNLOCKING POTENTIAL FOR MAXIMIZATION OF RECYCLING THROUGH SEPARATION OF MIXED WASTE FRACTIONS
Despite existing systems and infrastructure for source separation of consumer packaging waste, which the European citizens have access to, substantial amounts of recyclables are not correctly sorted and become part of mixed municipal waste. With the objective to meet minimum collection targets and reduce climate impact, many entities managing municipal waste, have made an effort to separate recyclables from the mixed waste of the household waste. The hereby fact sheet presents examples from a few locations in Europe and gives clear indication regarding enormous potential in recruiting additional volumes of valuable recyclables from mixed waste stream.
FEDERATION OF MUNICIPALITIES, SÖRAB, SWEDEN
SÖRAB represents population of 525000 citizens and has responsibility for collection of mixed municipal waste and treatment of waste in environmentally sound manner. In addition to source separation of packaging waste, SÖRAB has built and has been operating a central sorting plant from mixed municipal waste with the objective to increase recycling of materials and reduce climate impact from incineration.

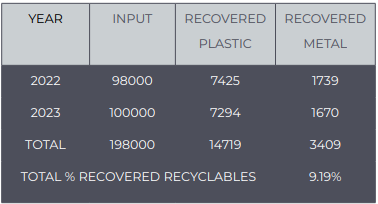 A significant portion of household waste consists of combustible waste (32%), food waste (27%), and garden waste (37%), with unsorted packaging fractions making up 30% of mixed waste. This highlights the need for efficient sorting and recovery systems to reclaim valuable materials. The table shows that in 2022 and 2023, a total of 198,000 tons of waste were processed, recovering plastic and metal. Overall, the percentage of recovered recyclables reached 9.19%.
A significant portion of household waste consists of combustible waste (32%), food waste (27%), and garden waste (37%), with unsorted packaging fractions making up 30% of mixed waste. This highlights the need for efficient sorting and recovery systems to reclaim valuable materials. The table shows that in 2022 and 2023, a total of 198,000 tons of waste were processed, recovering plastic and metal. Overall, the percentage of recovered recyclables reached 9.19%.
THE CITY OF GDAŃSK, POLAND
Gdańsk has made significant progress in waste management, particularly in recovering secondary raw materials from mixed waste. In 2023, the total municipal solid waste (MSW) amounted to 198,162 tonnes, with a recycling and reuse rate (including biodegradable waste) reaching 37.26%.

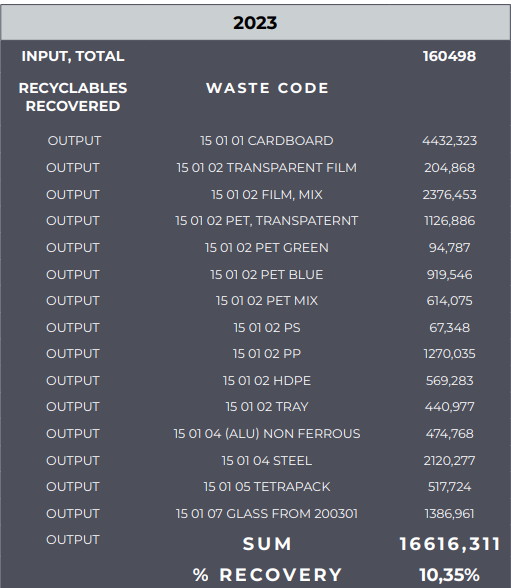
The volume of mixed waste processed for material recovery was 160,498 tonnes, from which 16,626 tonnes of secondary raw materials were extracted—accounting for 10.35% of the total mixed waste.
Recovered materials included:
- Plastic waste
- Glass
- Composite materials
- Metals
- Cardboard
The total amount of recovered secondary raw materials reached 16,616.31 tonnes.
THE CITY OF CRACOW, POLAND
Waste management is managed by MPO Krakow enterprise. Infrastructure for source separation of packaging waste located curbside includes bins for paper, glass, mixed plastic and metal packaging.In order to increase recycling rates, MPO Krakow has been recovering recyclables from mixed waste fractions (black
container) since 2024.

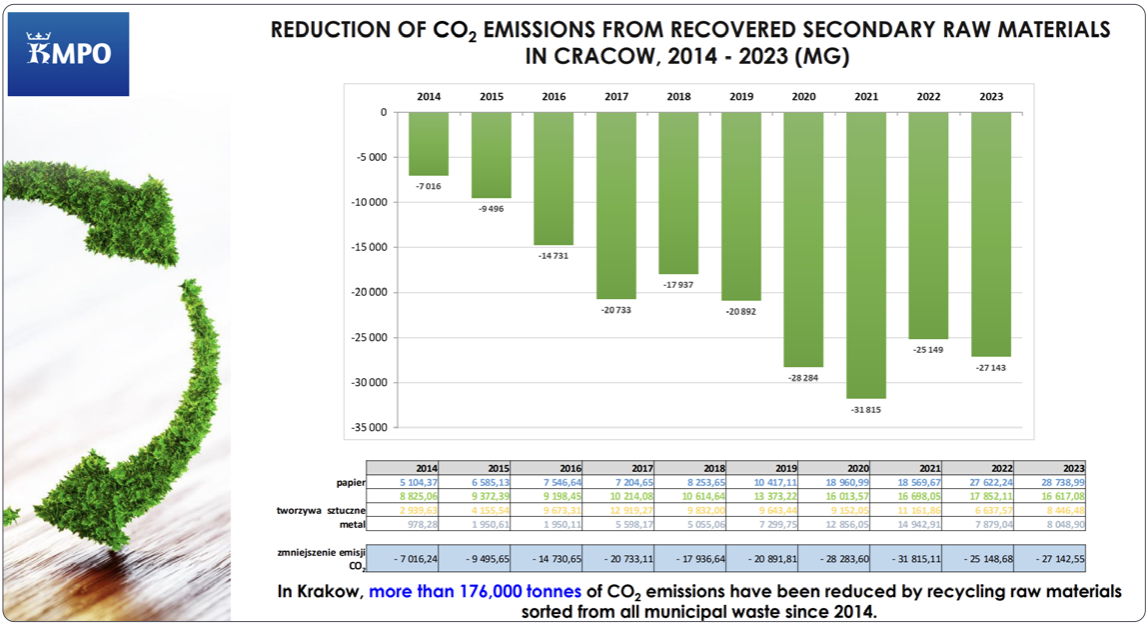
CO₂ Emission Reduction through Recycling of Secondary Raw Materials in Kraków (2014–2023)
From 2014 to 2023, Kraków reduced CO₂ emissions by over 176,000 tonnes through the recycling of secondary raw materials. The largest reduction was recorded in 2021, with 31,815 tonnes of CO₂, and in 2023, the reduction reached 27,143 tonnes. The main materials contributing to the reduction of emissions were paper, plastic, and metals. These results underscore the importance of waste separation and environmental initiatives in minimizing the impact on the environment.
CONCLUSIONS
The reference cases described in the hereby document confirm that additional separation of recyclables from the mixed waste fractions is already being implemented with the objective to increase amount of recyclables available for circular systems, increase recycling rates as well as to reduce climate impact of waste disposal. While the recyclables from additional sorting become a desired input material for recycling, the lack of recognition of the auxiliary separation method through mixed waste sorting, leads to uneven economic level playing field between producers who utilize supplementary resources and municipalities/waste processing entities making effort to separate additional waste. Because of the predicted growth of plastic packaging, limitations of source separation systems targeting lightweight packaging formats as well as potential to maximize yilds of separated recyclables, central sorting of mixed waste fraction becomes an important source of additional substrates for packaging circularity.

 Українська
Українська